Choosing Hearing Protection PPE: Earplugs vs Ear muffs | Disposable vs Reusable
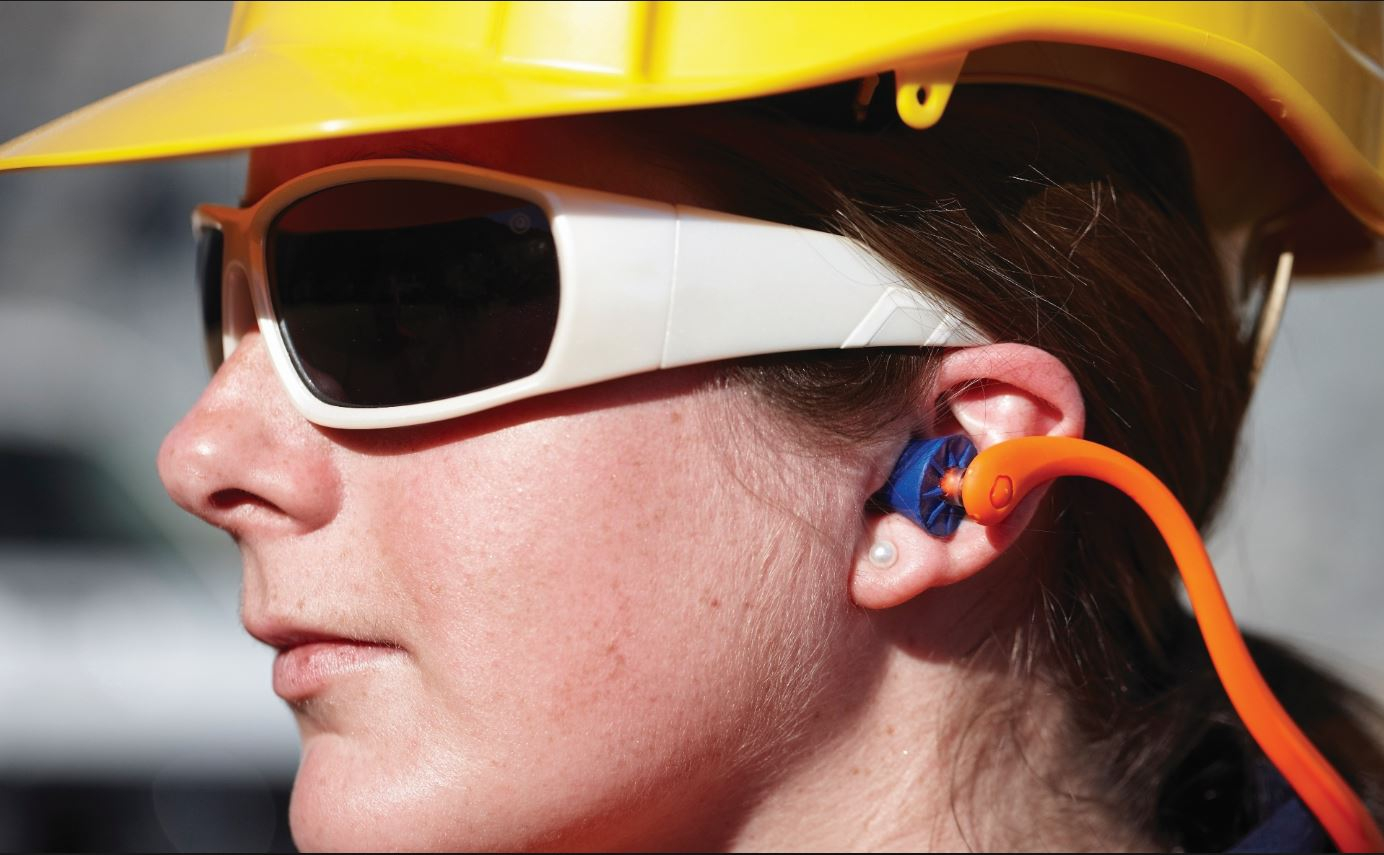

Hearing loss due to industrial noise such as machinery, tools and traffic is one of the most widespread yet preventable workplace injuries.
Hearing damage is irreversible and seriously affects quality of life, contributing to dementia, stress, hypertension, tinnitus (ringing in the ears) and psychiatric disorders.
Furthermore, a five-year (1999-2004) study of 6307 workers found that workers who are persistently exposed to excessive occupational noise may be two-to-three times more likely to suffer from serious heart disease than workers who were not exposed.
Hearing loss can also contribute to other workplace safety problems, such as a lack of awareness and reduced concentration and leads to around 3400 successful workers compensation claims each year.
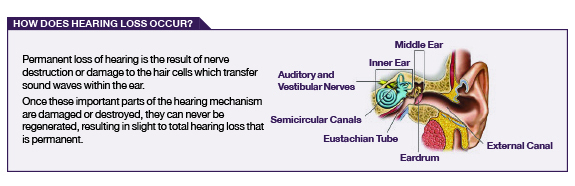 The good news is that hearing damage is entirely preventable with appropriate PPE. Correctly designed and fitted ear protection will keep industrial noise well below harmful levels, however choosing the appropriate hearing protection – whether ear muffs or ear plugs, disposable or reusable – is critical.
The good news is that hearing damage is entirely preventable with appropriate PPE. Correctly designed and fitted ear protection will keep industrial noise well below harmful levels, however choosing the appropriate hearing protection – whether ear muffs or ear plugs, disposable or reusable – is critical.
The "Safe Noise Threshold" and choosing the right level of protection
Eighty five decibels (85dB) is considered the “Safe Noise Threshold” and the level at which appropriate hearing protection MUST be worn. “Appropriate” is determined by the level of noise (see Figure 1) and required level of workplace communications.
Too much hearing protection may increase workplace dangers by unnecessarily blocking critical communications or noise – a common reason workers choose not to use any hearing protection at all.
Conversely, under-protection will lead to hearing damage, which is compounding as it leads to greater difficulty communicating while wearing hearing protection and thus a greater reluctance to wearing it.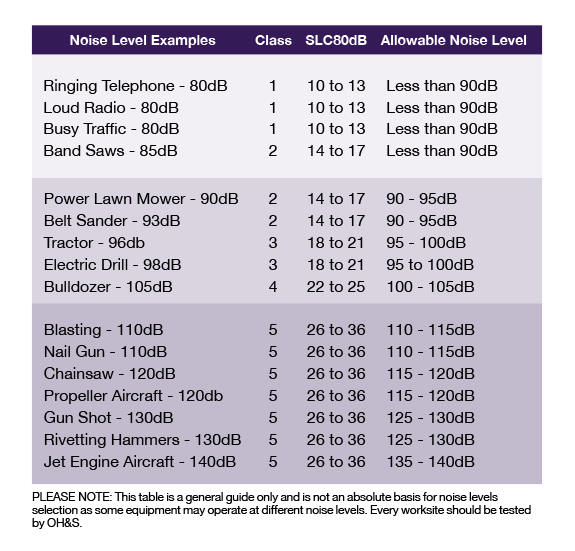
Hearing Protection Testing and Standards
Australian Standards AS/NZS 1270:2002 sees hearing protection rated into five classes, with Class 1 being the lowest level of protection and Class 5 being the highest level.
The system is based on the SOUND LEVEL CONVERSION (SLC80) rating which is the difference between the sound level of the environment in which the hearing protection is worn and the sound level reaching the wearer’s ears. This is converted to a Recommended Noise Range.
(Figure 1)
|
Class |
SLC80dB |
Recommended Noise Range (dB) |
|
1 |
10 – 13 |
Less than 90 |
|
2 |
14 – 17 |
90 – 95 |
|
3 |
18 – 21 |
95 – 100 |
|
4 |
22 – 25 |
100 – 105 |
|
5 |
26 – 36 |
105 – 140 |
Other Hearing Protection Choice Factors
As well as noise volume and communication factors, other considerations should include the hearing protection’s fit and comfort, health and hygiene, compatibility with other PPE such as hard hats, and suitability of the PPE for the worker, the work environment and task.
Earmuffs
Suppress unwanted noise by completely covering the outer ear. Our styles come with a variety of features from adjustable headband to hard hat attachments to suit individual needs.
-
-
-
3M PELTOR X Series Earmuff Helmet Attachment Class 5 SLC80 27dB (X4P3G/E)
Regular Price: $59.95
NOW: $54.95
-
3M Peltor X5A Premium Headband Earmuff Class 5 (X5A 290)
Regular Price: $67.50
NOW: $59.95
Disposable Earplugs
Made from PU foam and are designed to be compressed and then inserted into the ear canal, where they expand and seal against noise. These are economical, designed for single use and are available in uncorded and corded options.
Reusable Earplugs
Pre-moulded from washable silicone to fit snugly. Corded and uncorded options are supplied in handy resealable plastic case and can be reused.
Banded Earplugs
A convenient, easily inserted option for those who are constantly in and out of noisy areas.
Metal Detectable Earplugs
Contain a metal tab in each plug and a metalised cord that can be detected if they accidentally fall into processing lines.
Hearing Protection Fitting and Maintenance Guide:
Hearing protection – especially disposable earplugs – can cause ear infections if the correct health, hygiene and fitting formula is not followed correctly.
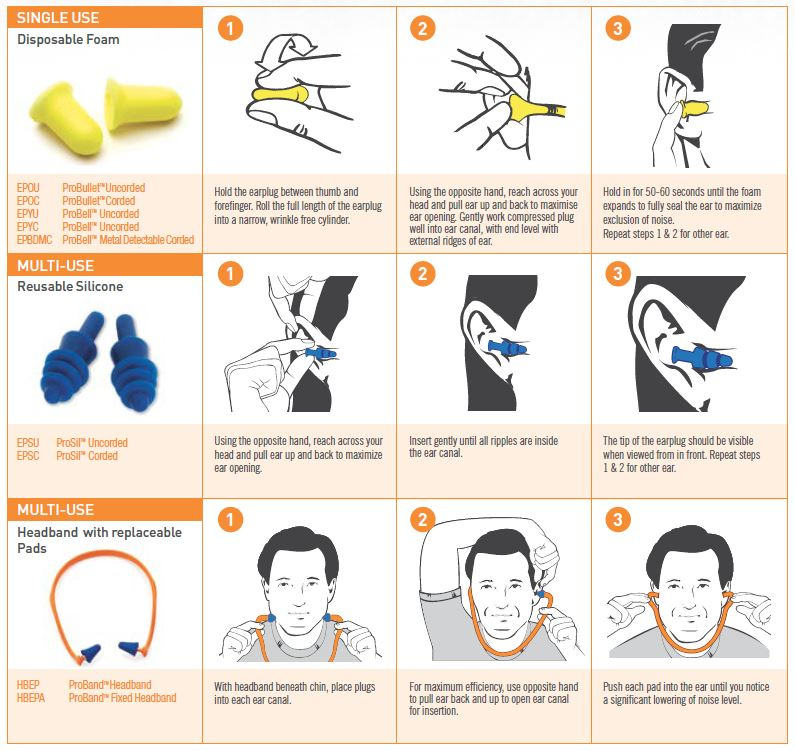
Earplug Maintenance:

Figure 3
Before handling earplugs, always wash and dry your hands. Then inspect your earplugs and discard them if damaged, worn or dirty. Reusable silicone earplugs will last up to three weeks if kept clean and undamaged. They should be cleaned with mild soap and water and stored in a case away from extreme heat or sunlight. When using banded earplugs, clean and replace the pads regularly, as required.
Earplug Fit and Removal:
When fitting earplugs, follow the fitting instructions outlined in Figure 2 and perform the fit test outlined in Figure 3. If either earplug feels incorrectly fitted, remove and re-insert.
When removing, gently twist the earplug while slowly pulling in an outward motion.











